Russian timber and pulp producers have requested the Ministry of Industry and Trade to create an emergency task force, warning that the industry faces shutdown risks following a 13% decline in logging volumes in 2024 compared to 2021. Pulp production dropped 3%, lumber output fell 11%, and plywood manufacturing plummeted 23%, highlighting pressure across the sector. The appeal was submitted by the Russian Association of Pulp and Paper Industry Enterprises, reports Kommersant newspaper.
The ruble appreciated by 22% against the dollar in the first half of 2024, and continued to strengthen in 2025 rising another 21% from January to June. Compared to June 2024, the ruble gained 10% by June 2025. Export-focused businesses report this currency strength, combined with a rise in the corporate profit tax from 20% to 25% and persistently high interest rates, has rendered many shipments unprofitable.
Image: Russian ruble fell from 72 to 102 per USD in
2024 due to imports, capital outflows, and weak
repatriation control / Central Bank of Russia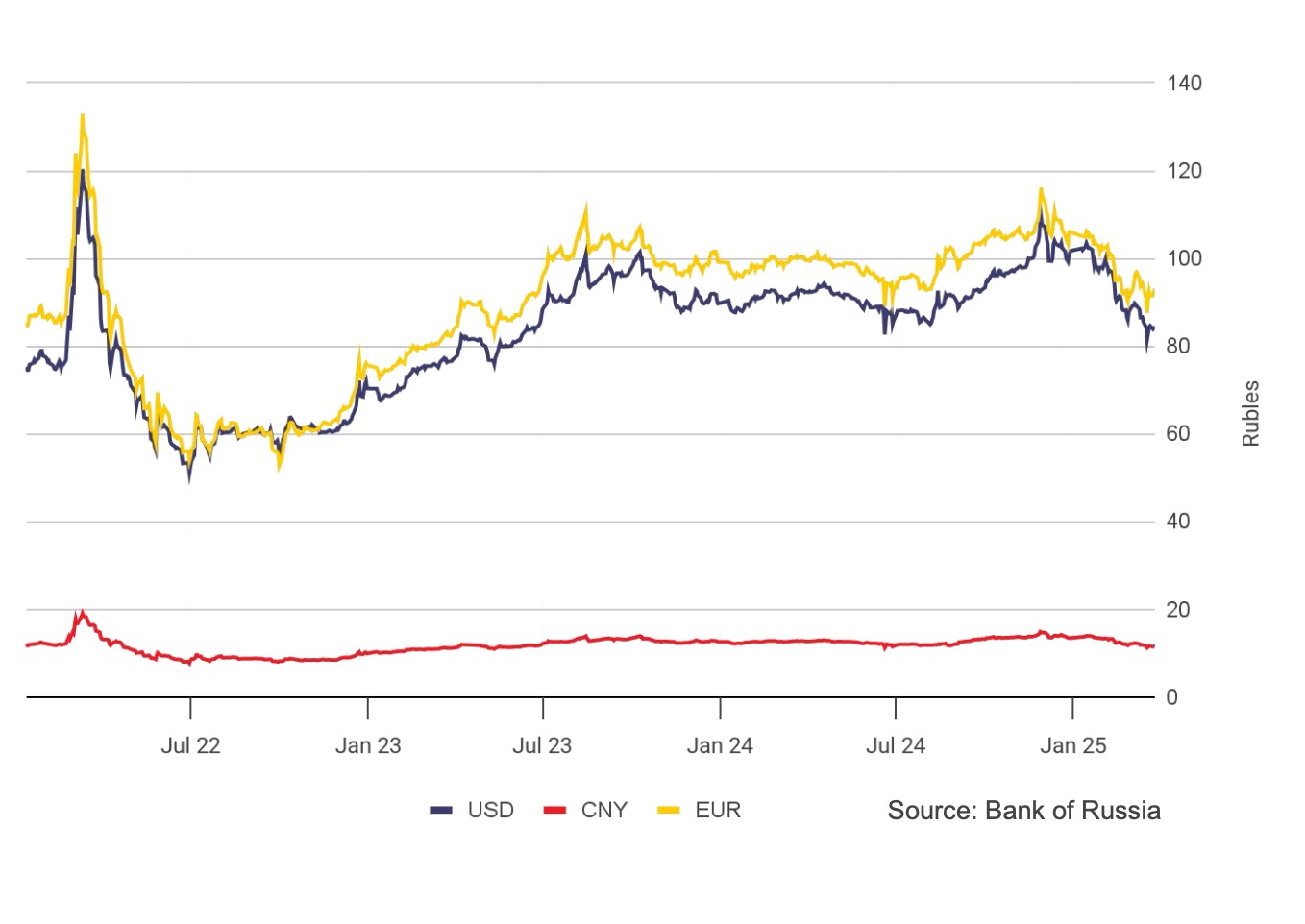
The industry notes that firms involved in mechanical wood processing, such as sawmills, were hit first, particularly after losing access to European Union markets. Between 2023 and 2024, major players like Segezha Group and ULK restructured debt due to low output, weak prices, and mounting costs. By mid-2024, these issues expanded to pulp and paper manufacturers, with losses intensifying as export margins disappeared and internal demand failed to compensate.
Executives report that some product lines, including pellets, pulpwood, and wood chips, now face virtually no market. Prices for lumber have continued to decline, while container freight rates for exports have sharply increased. The weak dollar exchange rate paired with expensive logistics has further damaged export profitability.
Lesprom Network, presenting at the Global Softwood Log & Lumber Conference in Vancouver in June 2025, reported that Russian sawmills have failed to fully replace lost EU sales. In January–May 2025, Russia’s softwood lumber exports to China fell 8% year-on-year to 4.37 million m3. China remains Russia’s top lumber market, but its construction slowdown continues to curb demand.
Image: China’s real estate sales, based on Lesprom Network’s Russian Lumber Industry Insights and China’s National Bureau of Statistics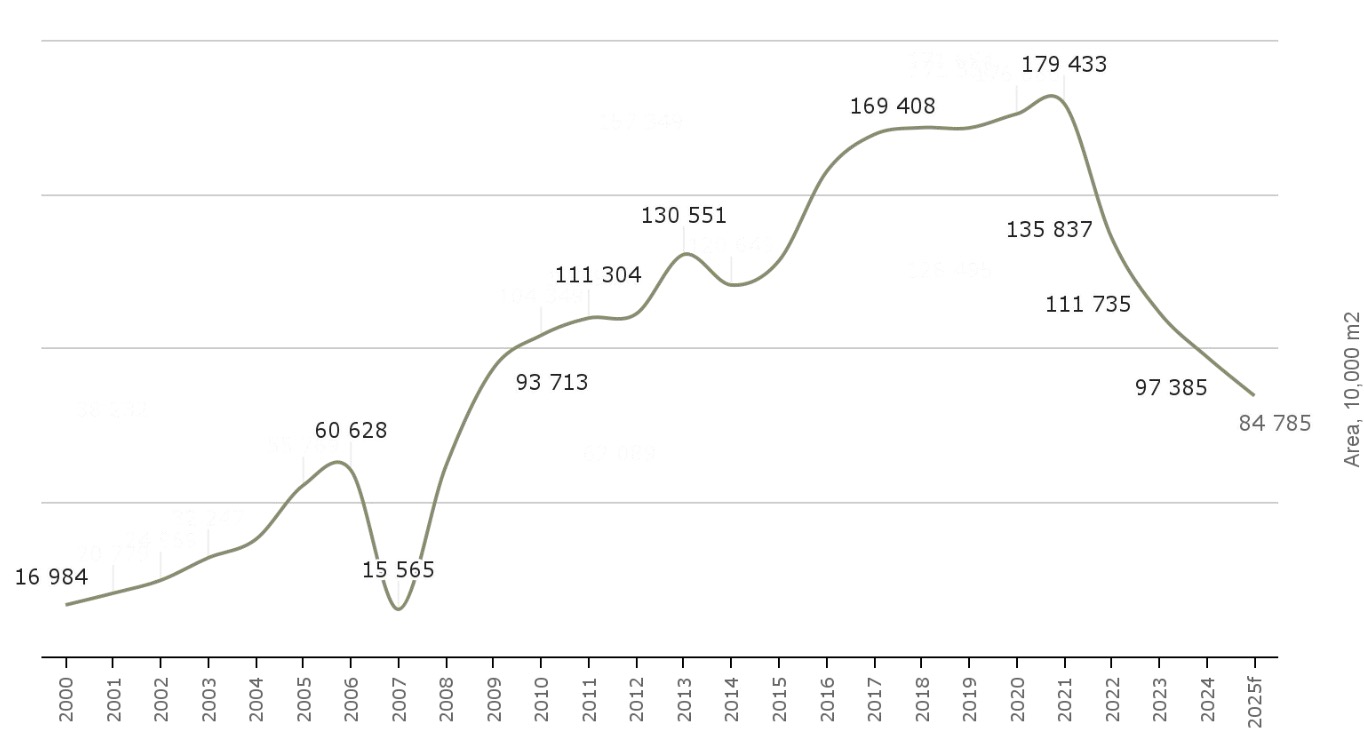
The construction downturn inside Russia continues to pressure the domestic market. In May 2025, construction volume fell 12% from April and 17% year-on-year. Lumber production mirrored this decline, down 9% from April and 2% from May 2024. Logging also dropped, falling 18% month-on-month and 5% year-on-year, according to the Russian Lumber Industry Insights report.
Domestically, high interest rates and the end of preferential mortgage programs pushed Russian mortgage rates to 28%, sharply reducing housing demand. Borrowing costs now absorb about 25% of sawmill profits, while inflation, rising production costs, and labor shortages have squeezed margins to roughly 4%. Increased rail tariffs have added further pressure to logistics costs.
In its appeal, the association warned that without immediate support, many producers risk halting operations in the second half of 2025. The proposal includes forming a dedicated task force within the ministry, chaired by Minister Anton Alikhanov, to monitor the situation and coordinate recovery measures.
Segezha Group attributes ongoing losses to “a difficult economic environment” shaped by reduced exports, weak construction activity, soft demand, and surging logistics tariffs. The company also cited declining operational efficiency across sites. It argues that monetary easing could stimulate recovery by improving credit access and domestic demand.
